Les copier/coller – Swift
Contenu
- Afficher une trace
- Chaîne de caractères
- Chaîne de caractères avec interpolation
- Chaîne – concaténation
- Créer un tableau à partir d’un fichier de propriétés
- Charger une image par programmation
- Cacher la barre d’état (haut de l’écran)
- Lire la sélection d’un UISegmentedControl
- Libre
- Revenir à la scène précédente
- UITableView – délégation
- Afficher une UITableViewCell perso
- UICollectionView – délégation
- Créer une tableau d’images à partir de fichiers\(i).png et animer
- Créer une image à partir d’une URL – Solution bloquante et non bloquante
- Créer une tableau à partir d’un résultat JSON via le web
- Préparer un segue
- Exécuter une méthode après un délai
- Programmer un NSTimer
- Afficher un Alert
- Charger une scène (NIB, XIB, View) par programmation
- Animer une propriété
- Détecter une collision entre deux UIView
- Insérer une ‘View’ dans une ‘View’ parent, à la position parentViewCount – n
- Obtenir l’élément d’un dictionnaire
- Array – codé au dur
- Array – énumération rapide
- Dictionnary – codé au dur
- Dictionnary – énumération rapide
- Afficher heure actuelle avec format
- Créer un UIButton + event par programmation
- Capturer l’écran dans un UIImage
- Poster vers Facebook
- Poster vers twitter
- Masquer le clavier
- Programmer une délégation (UITextField)
- Ajouter la gestion des versions à un projet existant
- Stub AppDelegate.swift pour Xcode 6.4
- Git à partir du terminal (pour un projet en équipe)
- Variables globales
- Prendre une pause
1. Afficher une trace
println("Bonjour le monde...")
let pi = 3.141592
println("La valeur de pi est \(pi)")
let a=3, b=7
println("\(a) + \(b) = \(a+b)")
let unNom = "TIM le magnifique"
print("\(unNom) dit: Bonjour ");print("à tous!\n")
2. Chaîne de caractères
let uneChaineRO = "Je suis une chaine en lecture seule"
var uneChaineRW = "Je suis une chaine en lecture écriture"
var uneChaineOC:NSString = "Je suis une chaine Objective-C"
println("Il y a \(countElements(uneChaineRO)) caractères dans uneChaineRO")
println("Il y a \(String(uneChaineOC.length)) caractères dans uneChaineOC")
3. Chaîne de caractères avec interpolation
let perso = "Fantomas" let persoForce = 17 var message = "Mon nom est \(perso) et j'ai \(persoForce) de force."
4. Chaîne – concaténation
var msg:String
let pi = 3.141592
msg = "Bienvenue " + "Au cours d'intro "
msg += "du langage Swift. PI = " + String(pi)
var res = ""
for car in msg {
res += car
}
5. Créer un tableau avec un fichier
// Étant donné le fichier suivant:
<array>
<dict>
<key>nom</key>
<string>Paul</string>
<key>photo</key>
<string>image01.png</string>
<key>dette</key>
<real>10.99</real>
</dict>
...
</array>
// Créer un tableau avec méthode: Swift + Foundation
let pathFichierPlist = NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("liste des amis", ofType: "plist")!
amis = NSArray(contentsOfFile: pathFichierPlist)
/// Méthode 100% swift (pas encore au point en version beta)
var tabloPerso:String[] = []
let path = NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("personnages", ofType: "plist")
tabloPerso = NSArray(contentsOfFile: path) as String[]
println(tabloPerso)
tabloPerso.append("Tintin")
println(tabloPerso)
println(tabloPerso[tabloPerso.count - 1])
// Créer un tableau de 'Dictionary' à partir d'un fichier plist
// Définition du tableau
var amis:[Dictionary<String,String>]!
...
// Affectation à partir d'un fichier
amis = NSArray(contentsOfFile: NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("liste des amis", ofType: "plist")!) as [Dictionary<String,String>]
6. Charger une image par programmation
let _image = UIImage(named:"paysage") self.uneImage.image = image // ou bien self.imageView.image = UIImage(named:"image.png")
7. Cacher la barre d’état (haut de l’écran)
override func prefersStatusBarHidden() -> Bool {
return true
}
8. Lire la sélection d’un UISegmentedControl
let selection =(sender as UISegmentedControl).selectedSegmentIndex
9. Libre
10. Revenir à la scène précédente
@IBAction func retourParent(sender: AnyObject) {
self.dismissViewControllerAnimated(true, completion:nil);
}
11. UITableView – délégation
// ********************************************************************
func tableView(tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection:NSInteger) -> Int
// ********************************************************************
{
return tablo.count
} // numberOfRowsInSection
// ********************************************************************
func tableView(tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> UITableViewCell!
// ********************************************************************
{
//variable type is inferred
var cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier("CELL") as? UITableViewCell
if !cell {
cell = UITableViewCell(style: UITableViewCellStyle.Value1, reuseIdentifier: "modeleCellule")
} // !cell
//we know that cell is not empty now so we use ! to force unwrapping
cell!.textLabel.text = tablo[indexPath.row]
cell!.detailTextLabel.text = "Personnage de Tintin"
cell!.imageView.image = UIImage(named:"lezard")
return cell
} // cellForRowAtIndexPath
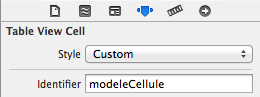
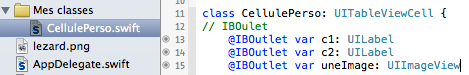
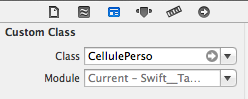
12. Afficher une UITableViewCell perso
// ********************************************************************
func tableView(tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> UITableViewCell!
// ********************************************************************
{
//Le type de la variable est inféré.
var cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier("modeleCellule") as? CellulePerso
if cell !=nil { // Si nil alors
cell = CellulePerso(style: UITableViewCellStyle.Value1, reuseIdentifier: "modeleCellule")
} // !cell
//À ce point ci, cell n'est pas nil. Il faut utiliser ! pour la déballer
cell!.c1.text = tablo[indexPath.row]
cell!.c2.text = "Personnage de Tintin"
cell!.uneImage.image = UIImage(named:"lezard")
return cell
} // cellForRowAtIndexPath
13. UICollectionView – délégation
// ********************************************************************
func collectionView(collectionView: UICollectionView?, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int
// ********************************************************************
{
return tablo.count
}
// ********************************************************************
func collectionView(collectionView: UICollectionView?, cellForItemAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath?) -> UICollectionViewCell?
// ********************************************************************
{
let cell = collectionView?.dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier("uneCellule", forIndexPath: indexPath) as CellulePersoCV
// Configuration de la cellule
cell.c1.text = String(itemCourant)
cell.c2.text = String(indexPath!.row)
cell.c3.text = tablo[indexPath!.row]
return cell
}
14. Créer une tableau d’images à partir de fichiers000(i).png et animer
let DUREE_ANIMATION = 1 as NSTimeInterval
let ANIMATION_NB_FOIS = 3
var tabloImages = UIImage[]()
for i in 1...28 {
tabloImages.append(UIImage(named:"warrior_walk_\(i).png"))
}
// Renseigner l'image à partir du tableau et démarrer l'animation
uneImageAnimee.animationImages = tabloImages
uneImageAnimee.animationRepeatCount = ANIMATION_NB_FOIS
uneImageAnimee.animationDuration = DUREE_ANIMATION
uneImageAnimee.startAnimating()
15. Créer une image à partir d’une URL
// Créer un UIImage à partir du WEB
// Solution bloquante
// ** Solution 1: Forme courte
let uneURL:NSURL = NSURL(string:"http://hmp.me/dtm")
uneImageURL.image = UIImage(data:NSData(contentsOfURL:uneURL));
// ** Solution 2: Forme longue avec validation
let uneURL:NSURL = NSURL(string:"http://hmp.me/dtm")
var err:NSError?
let htmlData = NSData.dataWithContentsOfURL(uneURL, options: NSDataReadingOptions.DataReadingMappedIfSafe, error: &err)
uneImageURL.image = UIImage(data:htmlData)
// ** Solution 3 - non bloquante
let uneURL:NSURL = NSURL(string:"http://hmp.me/dtm")
let request:NSURLRequest = NSURLRequest(URL:uneURL)
let queue:NSOperationQueue = NSOperationQueue()
NSURLConnection.sendAsynchronousRequest(request, queue: queue, completionHandler:{ (response: NSURLResponse!, data: NSData!, error: NSError!) -> Void in
self.uneImageURL.image = UIImage(data:data)
})
16. Créer une tableau à partir d’un résultat JSON via le web
// Obtenir la météo de Montréal via l'API Yahoo
let urlString = "http://query.yahooapis.com/v1/public/yql?q=select%20item%20from%20weather.forecast%20where%20location%3D%22CAXX0301%22&format=json"
let request:NSURLRequest = NSURLRequest(URL:NSURL(string: urlString))
let queue:NSOperationQueue = NSOperationQueue()
NSURLConnection.sendAsynchronousRequest(request, queue: queue, completionHandler:{ (response: NSURLResponse!, data: NSData!, error: NSError!) -> Void in
var err: NSError?
var jsonResult = NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: NSJSONReadingOptions.MutableContainers, error: &err) as NSDictionary
if(err?) {
// Si erreur de conversion JSON alors afficher l'erreur
println("JSON Error (err!.localizedDescription)")
}
println("===> résultat JSON:\n\n \(jsonResult)")
})
17. Préparer un segue
// Lancée automatiquement avant une transition 'segue'
// -------------------------------------------------------------
// Exemple pour une sélection à partir d'un UITableView
// ********************************************************************
override func prepareForSegue(segue: UIStoryboardSegue!, sender: AnyObject!)
// ********************************************************************
{
// Pointer sur la scène de destination
let sceneDestination = segue.destinationViewController as ClasseSceneDestination
// sender -> pointe sur la cellule sélectionnée
let selectionCourante = self.unTableView.indexPathForCell(sender as UITableViewCell).row;
// Envoyer les informations à la scène de destination
sceneDestination.tablo = tablo
sceneDestination.itemCourant = selectionCourante
} // prepareForSegue
// -------------------------------------------------------------
// Exemple pour une sélection à partir d'un UICollectionView
var _selection = 0
// ********************************************************************
override func prepareForSegue(segue: UIStoryboardSegue!, sender: AnyObject!)
// ********************************************************************
{
// Pointer sur la scène de destination
let sceneDestination = segue.destinationViewController as Scene03
// indice cellule sélectionnée via shouldSelectItemAtIndexPath
let selectionCourante = _selection;
// Envoyer les informations de la sélection courante
sceneDestination.title = tablo[selectionCourante]
}
// ********************************************************************
func collectionView(collectionView: UICollectionView?, shouldSelectItemAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath?) -> Bool
// ********************************************************************
{
_selection = indexPath!.row
return true
}
18. Exécuter une méthode après un délai
dispatch_after(temps, dispatch_get_main_queue(),
{
self.tournerLaPage("page2")
}
)
// ****************************************************
func tournerLaPage(scene:String) {
println("Tourner la page à \(scene)")
performSegueWithIdentifier(scene, sender: self)
}
19. Programmer un NSTimer
var unTimer:NSTimer!
...
unTimer = NSTimer.scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval(2, target: self, selector: Selector("uneFonction:"), userInfo: nil, repeats: true)
...
// *************************************
func uneFonction(timer: NSTimer) -> Void
{
println("Fonction exécutée par le timer...")
}
20. Afficher un Alert
// Nouvelle méthode proposée avec Swift
let alert = UIAlertController(title: "Title", message: "Message", preferredStyle: UIAlertControllerStyle.Alert)
alert.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "Button", style: UIAlertActionStyle.Default, handler: nil))
self.presentViewController(alert, animated: true, completion: nil)
// Ancien méthode inspirée d'Objective-C
var alert2 = UIAlertView()
alert2.title = "Un titre"
alert2.message = "Un message"
alert2.addButtonWithTitle("ok")
alert2.show()
21. Charger un NIB par programmation
var uneView = UINib(nibName: "Magazine01", bundle: nil).instantiateWithOwner(nil, options: nil)[0] as UIView // Pour ajouter à la scène courante: view.addSubview(uneView);
22. Animer une propriété
animerImage(self.uneImage)
// ****************************************
func animerObjet (objet:UIView){
UIView.animateWithDuration(
2,
animations: { objet.alpha = 0.5 },
completion: { finished in
objet.hidden = false }
) // UIView
UIView.animateWithDuration(
1,
delay:1,
options:UIViewAnimationOptions.CurveEaseIn,
animations: { objet.center.x = objet.center.x + 50},
completion: { _ in
// Code à exécuter lorsque animation terminée
// Par exemple, une autre animation.
}
) // UIView
} // animerImage
23. Détecter une collision entre deux UIView
CGRect personnage = [[lePersonnage.layer presentationLayer]frame];
CGRect sousZone = CGRectInset(personnage, personnage.size.width/2,personnage.size.height/2 );
if (CGRectIntersectsRect(sousZone, unObjet.frame))
{
NSLog(@"Il y a eu collision entre le personnage et %@", unObjet.class);
}
24. Insérer une subView à la position parentViewCount – n
view.insertSubview(uneView, atIndex: view.subviews.count - 1)
25. Obtenir l’élément d’un dictionnaire
if let tt = jsonResult["query"]!["results"]!["channel"]!["item"]!["condition"]!["temp"]! as String!
{
println("Température actuelle pour Montréal: \(tt)")
}
26. NSArray – créer au dur
var tablo = ["Bob", "Binne", "Tintin", "Milou", "Hadock", "Castafiore", "Allan", "Tounesol", "Alcazar", "Barnabé", "Baxter", "Bill","Bohlwinkel", "Cipaçalouvishni"]
// Pour ajouter un élément
tablo.append("Objectif Lune")
// Ou
tablo+="encore"
// Pour un NSArray
var tabloNSArray:NSMutableArray = ["Tintin", "et", "Milou"]
tabloNSArray.addObject("Coke en stock")
27. NSArray – énumération rapide
// Énumération des éléments d'un tableau
for item in tablo) {
println("Item: \(item)")
}
// Énumération des éléments d'un tableau avec indice
for (index, value) in enumerate(tablo) {
println("Item \(index + 1): \(value)")
}
28. NSDictionnary – créer au dur
var dictio = ["Nom":"Paul", "Age":22, "Titre":"Intégrateur", "Expérience":2] // Ajouter un élément dictio["Compagnie"] = "TIM" var dictio2:NSDictionary = ["Nom":"Paul", "Age":22, "Titre":"Intégrateur", "Expérience":2]
29. NSDictionnary – énumération rapide
//Pour parcourir les éléments d'un dictionnaire
for(NSString * key in unDictionnaire){
NSLog(@"clé: %@, contenu: %@", key, unDictionnaire[key]);
}
30. Afficher heure actuelle avec format
// ******************************************
func obtenirHeure() -> String {
let unFormateurDeDate = NSDateFormatter()
unFormateurDeDate.dateFormat = "'Nous sommes 'EEEE' et il est 'hh:mm:ss";
unFormateurDeDate.locale = NSLocale(localeIdentifier: "en_US_POSIX")
return unFormateurDeDate.stringFromDate(NSDate())
} // obtenirHeure
println(obtenirHeure())
// Ou en ajoutant une nouvelle méthode à la Classe NSDate
extension NSDate
{
convenience
init(dateString:String) {
let dateStringFormatter = NSDateFormatter()
dateStringFormatter.dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd"
dateStringFormatter.locale = NSLocale(localeIdentifier: "en_US_POSIX")
let d = dateStringFormatter.dateFromString(dateString)
self.init(timeInterval:0, sinceDate:d)
}
}
31. Créer un UIButton + event par programmation
// ********************************************************
func creerBouton(texte:String, action:String) -> UIButton {
let unBouton = UIButton.buttonWithType(UIButtonType.System) as UIButton
unBouton.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 50)
unBouton.backgroundColor = UIColor(red: 45/255, green: 23/255, blue: 111/255, alpha: 1.0)
unBouton.setTitle(texte, forState: UIControlState.Normal)
unBouton.setTitleColor(UIColor.whiteColor(), forState: UIControlState.Normal)
unBouton.addTarget(self, action: Selector(action), forControlEvents: UIControlEvents.TouchUpInside)
return unBouton
} // creerBouton
// ********************************************************
func boutonAction(sender:UIButton!)
{
println("Action du bouton maison!")
}
// Utilisation
self.view.addSubview(creerBouton("Victoire!", action: "boutonAction:"))
32. Copier l’écran dans un UIImage
// import QuartzCore
var imageFinale = UIImage()
func sauvegarderEcran(){
// Description : méthode servant à capturer l’écran et au besoin,
// en faire une sauvegarde dans l’album photos.
// 1 - Préparer un contexte de dessin à partir de la taille de la scène
UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(self.view.bounds.size);
// 2 – Dessiner à partir du claque par défaut de la scène
self.view.layer.renderInContext(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext());
// 3 – Stocker le résultat dans notre objet local
imageFinale = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext();
// 5 – Fermer le contexte de dessin
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
// 6 – Facultatif - Stocker une copie de la capture d’écran dans l’album photos
UIImageWriteToSavedPhotosAlbum(imageFinale, nil, nil, nil );
} // sauvegarderEcran
33. Poster vers Facebook
import Social
func posterSurFacebook() {
// Les étapes pour utiliser ‘facebook’
// 1 - Tester si le service et les informations de connexion sont dispo
if SLComposeViewController.isAvailableForServiceType(SLServiceTypeFacebook)
{
// 2 - Créer un feuille pour le 'post'
let controleur = SLComposeViewController (forServiceType: SLServiceTypeFacebook)
// 3 - Composer le message
controleur.setInitialText("Test avec Swift et Xcode");
// 4 - Ajouter une image - facultatif
controleur.addImage(imageFinale);
// 5 - Ajouter un lien - facultatif
controleur.addURL(NSURL(fileURLWithPath:"/cours/xcode/"))
// 6 - Présenter la fenêtre de confirmation à l'utilisateur
self.presentViewController(controleur, animated: true, completion: nil);
} // if Facebook
} // posterSurFacebook
34. Poster vers twitter
import Social
func posterSurTwitter() {
// Les étapes pour utiliser ‘twitter’
// 1 - Tester si le service et les informations de connexion sont dispo
if SLComposeViewController.isAvailableForServiceType(SLServiceTypeTwitter)
{
// 2 - Créer un feuille pour le 'post'
let tweetSheet = SLComposeViewController (forServiceType: SLServiceTypeTwitter)
// 3 - Composer le message
tweetSheet.setInitialText("TIM.CSTJ - Production sur support 2015. Intro à Swift #CSTJ");
// 4 - Ajouter une image - facultatif
tweetSheet.addImage(imageFinale);
// 5 - Ajouter un lien - facultatif
// [tweetSheet addURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@""]];
// 6 - Présenter la fenêtre de confirmation à l'utilisateur
self.presentViewController(tweetSheet, animated: true, completion: nil);
} // if twitter disponible ...
} // posterSurTwitter
35. Masquer le clavier
// Note: il faut aussi renseigner le 'delegate' de l'objet
func textFieldShouldReturn(textField:UITextField!) -> Bool{
textField.resignFirstResponder()
return true
}
36. Programmer une délégation (UITextField)
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, UITextFieldDelegate {
@IBOutlet weak var unChamp: UITextField!
var nbRetours = 0
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
unChamp.delegate = self
} // viewDidLoad
/// Programmer une délégation
func textFieldShouldReturn(textField: UITextField!) -> Bool {
println("La touche 'Return' a été appuyée \(++nbRetours) fois.")
return true
} //textFieldShouldReturn
} // ViewController
37. Ajouter la gestion des versions à un projet existant
# À partir de l'app 'terminal', naviguer vers le dossier parent du projet et saisir les commandes suivantes: git init git add . git commit -m "Premier 'Commit'"
38. Stub AppDelegate.swift pour Xcode 6.4
// AppDelegate.swift
// stub
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [NSObject: AnyObject]?) -> Bool {
return true
} // didFinishLaunchingWithOptions
func applicationWillResignActive(application: UIApplication) { }
func applicationDidEnterBackground(application: UIApplication) { }
func applicationWillEnterForeground(application: UIApplication) { }
func applicationDidBecomeActive(application: UIApplication) { }
func applicationWillTerminate(application: UIApplication) { }
} // class AppDelegate:
39. Git à partir du terminal (pour le travail d’équipe)
Étapes: 1 - Creer un 'repo' sur github avec un Readme et ignore 'swift' 2 - Creer le projet sous Xcode avec l'option 'git' 3 - Avec terminal, cd vers le dossier du projet taper: git init git remote add origin https://github.com/votre compte/le projet.git git pull origin master git add * git commit -m "commit de depart" 4 - dand Xcode, faire un push // Pour le deuxieme membre de l'équipe faire: Source control -> check out // gestion des conflits http://roadfiresoftware.com/2015/09/automatically-resolving-git-merge-conflicts-in-xcodes-project-pbxproj/
40. Variables globales
Ajouter une classe ou une structure au projet qui contient des propriétés statiques:
// Fichier Static.swift
struct Static {
static var i = 99
}
/// Exemple d'utilisation:
override func viewDidAppear(animated: Bool) {
Static.i = 123
println(Static.i)
}